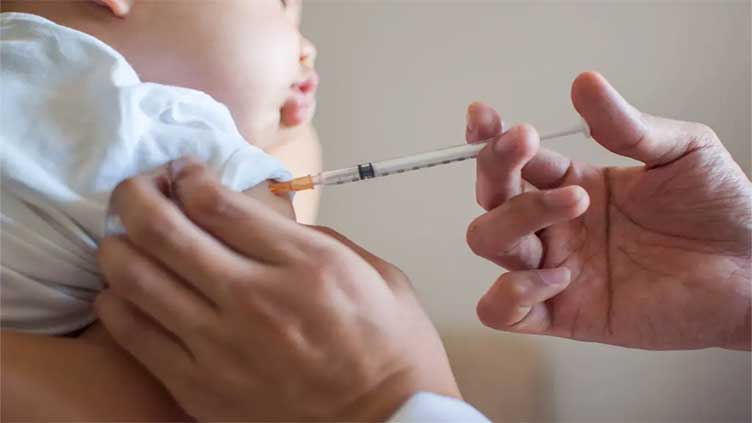
A brand new monoclonal antibody accepted via the meals and Drug administration (FDA) is effective at stopping severe illnesses and hospitalizations from RSV in infants, a new look at unearths.
In a real-world study of extra than 8,000 infants below 12 months, British researchers located that individuals who received Beyfortus have been less likely to require hospitalization due to a extreme contamination from RSV.
Normal, results recommend that the shot became nearly 90% powerful at preventing hospitalization and almost 76% powerful at preventing RSV-associated decrease respiratory tract infection.
Beyfortus, which uses the active element nirsevimab, is developed and synthetic via the pair of eu pharma giants AstraZeneca and Sanofi.
It turned into authorized with the aid of the FDA in July, and the facilities for sickness control and Prevention later endorsed the shot for toddlers 19 months and more youthful.
Even though nirsevimab is a shot, it isn’t taken into consideration an immunization and isn’t always a vaccine in the usual sense.
It is a monoclonal antibody treatment that exposes toddlers to RSV proteins, which, in turn, prepare their bodies to fight off an RSV contamination.
Also read: This smart typewriter promises distraction-free writing
The majority who’re uncovered to RSV will now not agreement a extreme illness. For wholesome adults, RSV might gift much like the manner a commonplace bloodless would, but for positive groups of people — toddlers and older adults — the virus can trigger a intense contamination.
The CDC estimates that there are more than 2 million outpatient visits amongst children younger than five because of RSV.
The virus additionally hospitalizes up to eighty,000 kids according to year and is responsible for as much as three hundred pediatric deaths yearly.
When Beyfortus became accredited, many professionals expressed their enthusiasm for the way the shot may want to mood the inflow of infection amongst children that provides during RSV season, which usually takes place between fall and spring.
But, a scarcity of the treatment has dampened doctors’ optimism.
In October, the CDC issued an advisory pronouncing that the shot could be in short deliver during the 2023-2024 season.
Round one month later, the CDC and FDA introduced plans to expedite the release of seventy 7,000 additional doses to help meet the call for.